
It doesn’t get much better than waking up refreshed after a full night’s rest. Yet, according to the American Sleep Association, over 35% of adults report not getting enough sleep each night.
If you are not taking sleep seriously, you should! According to the Center for Disease Control you are more likely to experience chronic health conditions if you are not getting enough.
What’s worse is that prescription sleeping pills, including hypnotic drugs such as Ambien are associated with greater risk of mortality. Those numbers get worse when you start mixing in opioids, alcohol, and other drugs.
It makes sense to us then to turn directly to our body’s own endocannabinoid system and to consider cannabis as a healthier solution.
shop sleep productsOur Endocannabinoid System
Named after the plant that led to its discovery, the endocannabinoid system is largely responsible for regulating our body, including the way we fall sleep, stay asleep, wake up, and remain awake.
Our body naturally makes endocannabinoids, such as anandamide and 2-arachidonoylglycerl (2-AG), which stimulate our cannabinoid receptors.

Phytocannabinoids are cannabinoids found in plants such as delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), cannabidiol (CBD), and cannabinol (CBN) which stimulate those same receptors. These molecules are very similar to the ones our own bodies produce.
While research has been blocked for decades due to outdated federal policies, it seems perfectly reasonable that so many people are turning to cannabis as a natural remedy to their sleep problems.
Cannabinoids & Dosing
Between research data and anecdotal accounts, we know THC and CBD have a biphasic dose response in respect to sleep which means they can both be alerting or sedating depending on the dosage.
- THC – Tetrahydrocannabinol is the main psychoactive cannabinoid in cannabis and is what gives weed its high.
- Sedative effects, making it easier to fall asleep
- May improve breathing during sleep
- Reduces time spent in REM sleep and increases slow-wave sleep, reducing nightmares
- CBD – Cannabidiol promotes relaxation without the high associated with THC.
- Reduces daytime sleepiness
- Increases total sleep time
- Decreases nighttime sleep interruptions
- CBN – Cannabinol is converted from THC as the cannabis plant ages and is similar to CBD in that it has no psychoactive effect or high. However, it may have strong sedative effects. CBN research is still very much in preliminary stages.
- May prolong sleep time
- Sedative effects are increased when combined with THC
Lower doses and a balance of THC and CBD are more likely to aid in your sleep problems. Look for a 1:1 CBD:THC preparation and adjust according to your experience. High doses may be overly stimulating for sleep. For both new and experienced users, add CBN to round out and enhance your effects.
- New Cannabis Users – Start with 2.5 mg of THC and CBD each.
- Experienced Cannabis Users – Try 5 to 15 mg of THC and CBD each.
Strains
Indica, Sativa, and Hybrid – Which is better for sleep? While Indica is generally considered to be the more relaxing and sedative variety, with Sativa being more energizing, those researching cannabis say that these generalizations are not totally accurate.
When it comes to sleep, and our individual responses to cannabis in general, the balance of cannabinoids and which terpenes are present in the strain hold greater significance.
Terpenes
Terpenes are molecules that create smell and taste in many plants, flowers, and fruits. There have been over 150 different terpenes identified and different combinations of these terpenes give cannabis strains their distinctive smells and flavors. Science is starting to show that terpenes also have different effects on our bodies.
Terpenes suggested to aid with sleep:
- Terpinolene – Citrus, Woody, Smoky
- Terpineol – Floral
- Nerolidol – Sweet, Rose, Fresh
- Phytol – Floral
- Limonene – Orange, Citrus
- Linalool – Floral, Sweet, Woody
- Myrcene – Sweet, Minty, Camphor
- Caryophyllene – Piney, Woody

Extra Ingredients
In addition to cannabinoids, some products contain other ingredients that may have beneficial effects for sleep and relaxation. Many of these ingredients are commonly found in health food stores and in teas.
- Melatonin
- Valerian Root
- Passionfruit
- Amino Acids
- Chamomile
- Magnesium
- Mushrooms
- Rose

Consumption Method & Duration
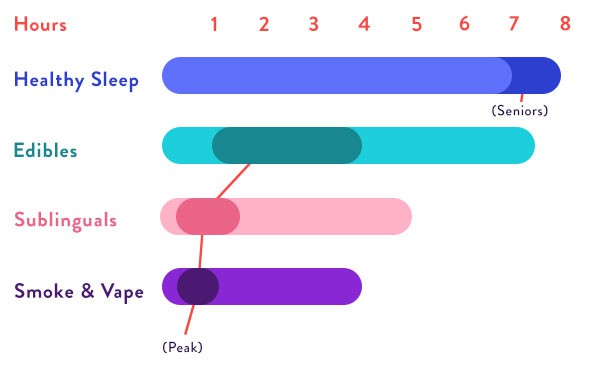
The modern cannabis industry has given us more options for consuming cannabis than ever before. Every method, from smokes, vapes, edibles, tinctures, sublingual strips, and more have different onsets, durations, and ingredient choices when it comes to sleep.
Side Effects
While cannabis can be a helpful tool for rest and sleep, it does come with side effects if not used carefully.
- Rare but possible “weed hangover” or morning grogginess with high-THC strains and overuse
- Possible withdrawal symptoms after stopping extending use which could affect mood and sleep, and may increase dreams
Other Tips
As with any other method of trying to improve sleep, creating a well-balanced routine in your life in addition to trying cannabis will only help.
- Take a break from alcohol
- Maintain healthy diet
- Exorcise regularly BWAHAHAHAHA
- Avoid caffeine and other stimulants 4-6 hours before bedtime
- Create a calm bedtime routine
- Consult your doctor / therapist
References
- NORML – Introduction to the Endocannabinoid System – https://norml.org/marijuana/library/recent-medical-marijuana-research/introduction-to-the-endocannabinoid-system/
- Project CBD – Cananbis & Sleep Disturbances – https://www.projectcbd.org/medicine/cannabis-sleep-disturbances
- Sleep Foundation – Alcohol and Sleep – https://www.sleepfoundation.org/nutrition/alcohol-and-sleep
